Simplify .NET Background Tasks Using Hangfire
Learn how to run background jobs efficiently in your .NET applications using Hangfire.This guide covers job types, scheduling, retries, and monitoring—no complex threading required.
Hangfire is a powerful, open-source framework for handling background jobs in .NET applications. It enables developers to create, manage, and execute background tasks seamlessly—without the need to write complex threading code or manage task lifecycles manually.
Whether you're scheduling periodic tasks or offloading long-running processes, Hangfire offers a robust and scalable solution for background job management.
🧱 Core Components of Hangfire
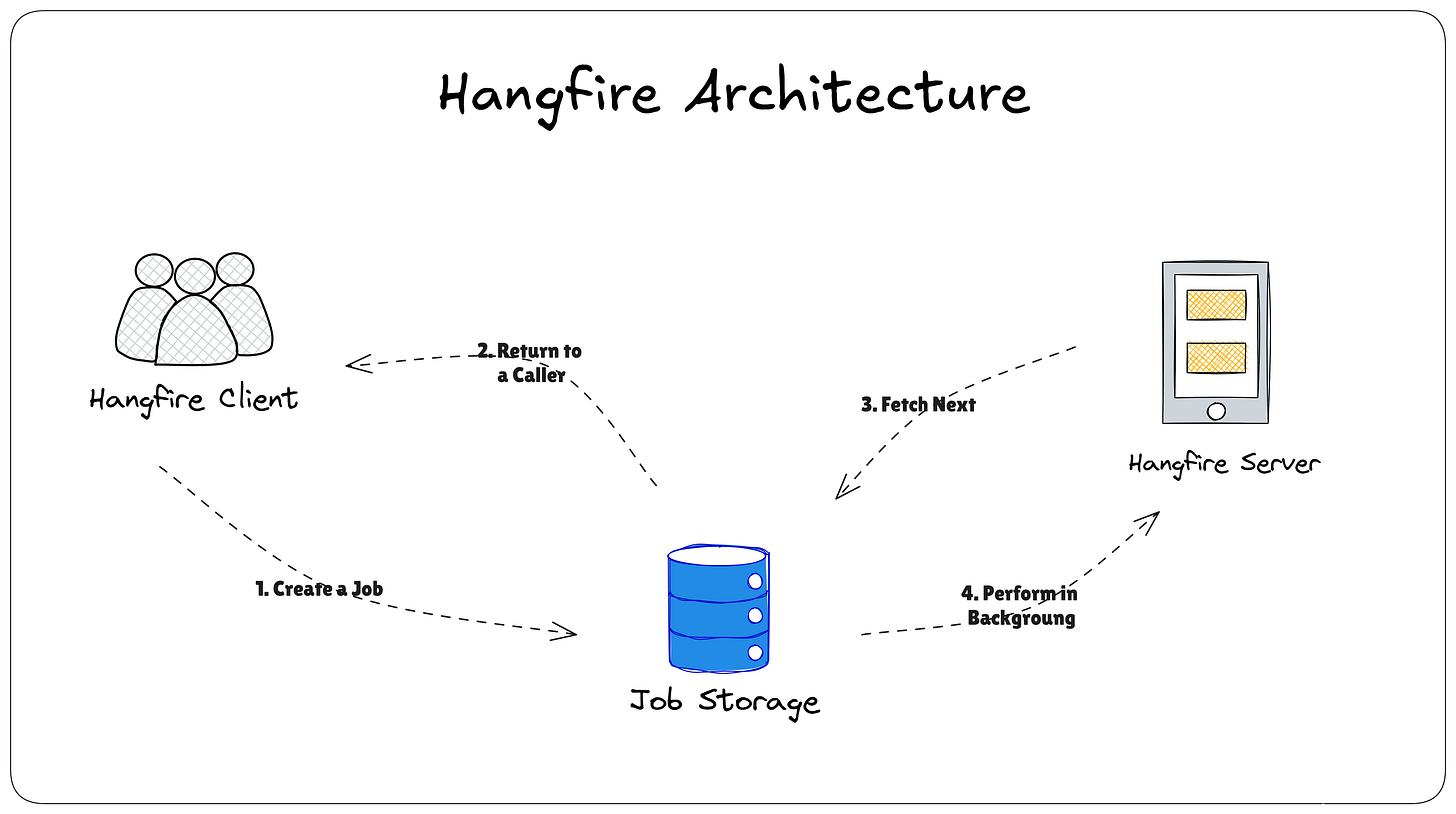
Hangfire is built around four key components that work together to provide a full-fledged background job system:
1. Dashboard
A built-in web interface that allows you to monitor and manage background jobs. You can view the job status, execution history, errors, retries, and manually trigger or delete jobs.
You can enable the dashboard in your application by adding this to your Startup.cs or Program.cs:
app.UseHangfireDashboard("/hangfire");Then access it at: http://localhost:<port>/hangfire
The dashboard is secured by default in production, and you can configure authorization with custom filters.
2. Server
The job-processing engine that continuously polls the job queue and executes background tasks. You can run multiple servers in a distributed setup for load balancing and high availability.
3. Storage
All job-related data—including status, history, retries, and parameters—are persisted in storage. Hangfire supports various storage backends, such as:
SQL Server
Redis
PostgreSQL (via third-party packages)
In-memory (not recommended for production)
4. Jobs
Jobs represent the actual tasks you want to run in the background. Hangfire supports several types of jobs (discussed below), making it suitable for both simple and complex workflows.
🚀 When to Use Hangfire?
Hangfire is ideal for scenarios where background execution or scheduling is required in .NET applications. Below are some real-world use cases:
1. Background Processing
Long-running tasks: Operations like report generation, video processing, or data transformation.
Non-blocking operations: Sending emails, uploading files, or image processing can be moved to the background to improve user responsiveness.
2. Task Scheduling
Recurring Jobs: Automatically run jobs on a fixed schedule (e.g., hourly, daily, weekly).
Delayed Jobs: Trigger a task after a predefined delay (e.g., send follow-up emails after 24 hours).
3. Task Coordination
Continuation Jobs: Chain multiple tasks, ensuring a job runs only after its predecessor completes successfully.
Batch Jobs (Pro): Group multiple jobs to execute in parallel or sequence.
Batch Continuations (Pro): Trigger a task once a batch has completed.
4. Scalability & Reliability
Distributed Job Processing: Run background workers across multiple servers to distribute workload.
Automatic Retries: Failed jobs are retried automatically based on configurable retry policies.
5. Enhanced User Experience
Faster UI Response: Background jobs ensure the UI remains fast by deferring heavy processing.
Real-time Updates: Use scheduled jobs to fetch or sync data periodically, keeping dashboards and reports up to date.
6. System Integration
Legacy Systems: Schedule periodic sync tasks for older systems.
Microservices: Background processing in service-to-service communication or event-driven systems.
🧩 Types of Jobs in Hangfire
Hangfire offers multiple job types to handle various execution scenarios:
✅ Fire-and-Forget Jobs
These jobs are executed once, immediately after being enqueued. They are useful for operations that don’t require instant feedback, such as logging or email notifications.
BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Executed once immediately."));⏰ Delayed Jobs
These are scheduled to run after a specified delay. For example, sending a follow-up email after a few hours.
BackgroundJob.Schedule(() => Console.WriteLine("Executed after 5 minutes."), TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5));🔁 Recurring Jobs
These jobs run on a schedule defined using CRON expressions. Ideal for tasks like daily backups or cleanup routines.
RecurringJob.AddOrUpdate("my-recurring-job", () => Console.WriteLine("Runs every day"), Cron.Daily);🔗 Continuation Jobs
A continuation job runs only after its parent job completes successfully. This helps build dependent workflows.
var parentJobId = BackgroundJob.Enqueue(() => Console.WriteLine("Step 1"));
BackgroundJob.ContinueWith(parentJobId, () => Console.WriteLine("Step 2 after Step 1"));📦 Batch Jobs (Hangfire Pro)
Allows grouping multiple jobs into a batch, which can then be processed in parallel or sequentially.
🔄 Batch Continuations (Hangfire Pro)
A job that runs only after all jobs in a batch are completed.
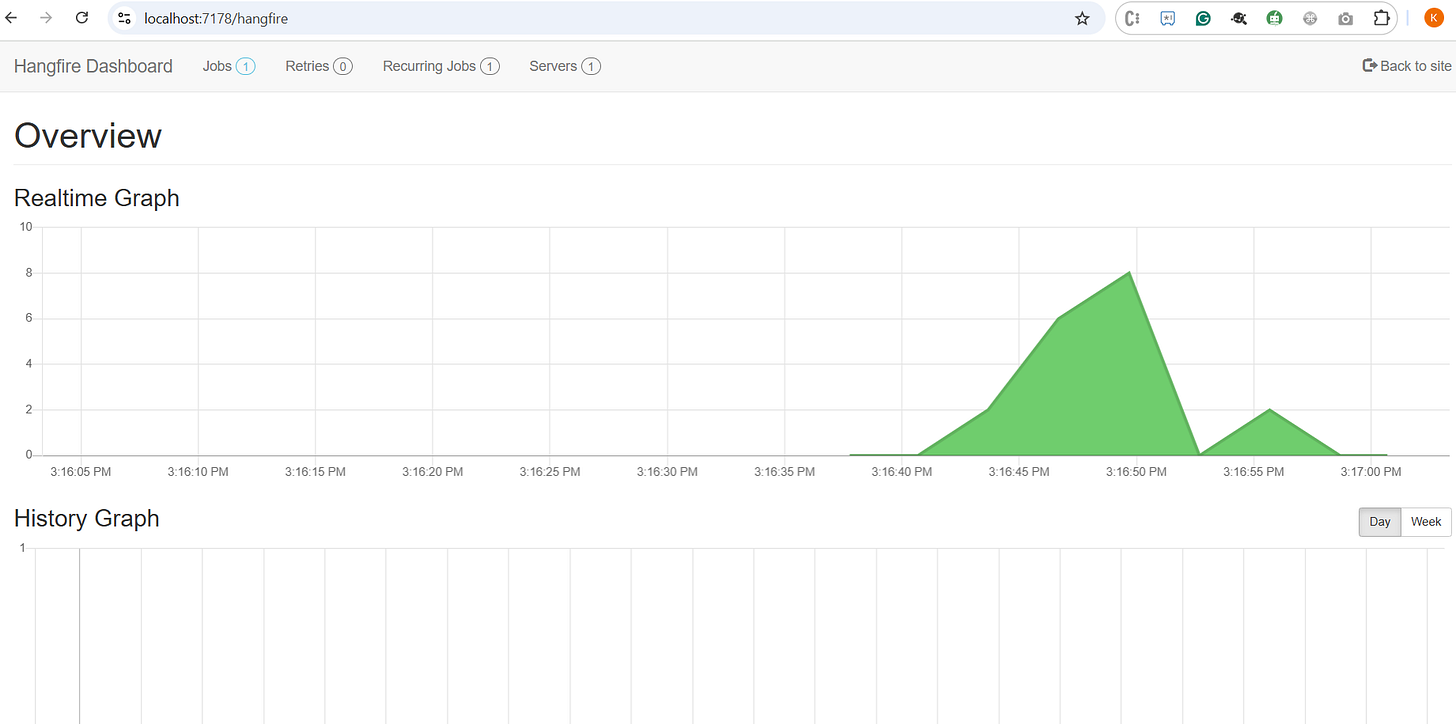
Hangfire dashboard
Open URL: https://localhost:7178/hangfire🔁 Alternatives to Hangfire
While Hangfire is highly capable, there are several alternatives depending on your use case and ecosystem:
✅ Quartz.NET
A mature, open-source job scheduling system suited for everything from small apps to large enterprise systems.
☁️ Azure Functions
A serverless compute option for background processing in Azure. Ideal for cloud-native applications.
📨 RabbitMQ + MassTransit
Combines message queuing with background job orchestration—great for microservices and distributed systems.
☁️ AWS Lambda
A serverless alternative similar to Azure Functions, but built for the AWS ecosystem.
🧩 .NET Core Hosted Services
A lightweight, built-in background task mechanism in .NET Core—great for simpler use cases, though with fewer features compared to Hangfire.
🧠 Summary
Hangfire makes it simple to add robust and scalable background job processing to your .NET applications. With built-in support for retries, scheduling, and monitoring, it drastically reduces development effort and improves application performance.
Whether you're handling background processing, scheduling recurring tasks, or managing complex workflows, Hangfire is a reliable and production-ready choice for .NET developers.
If Hangfire doesn’t fit your requirements, alternatives like Quartz.NET, Azure Functions, or RabbitMQ with MassTransit may serve your needs better depending on the architecture and complexity of your project.
Download Sample Code
https://sourcecode.kanaiyakatarmal.com/hangfire