🔐 JWT Explained: The Key to Stateless Authentication
Discover why JWT is the go-to solution for authentication in today’s distributed and fast-paced software world.
In a world where users bounce across apps, devices, and networks in milliseconds, secure and scalable authentication is no longer optional — it’s a necessity.
That’s where JWT (JSON Web Token) comes in — your API’s silent guardian. 🛡️
📦 What is JWT?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe token format used to securely transmit information between two parties — usually a client and a server.
Unlike traditional session-based authentication, JWT is stateless — meaning no server-side session storage is needed.
A typical JWT looks like this:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.
eyJ1c2VySWQiOiIxMjM0NTYifQ.
SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5cIt consists of three parts:
Header – Contains the token type and signing algorithm (e.g., HMAC SHA256).
Payload – Includes the claims or user data (e.g., user ID, role).
Signature – A cryptographic hash used to verify the token’s authenticity.
🧠 How Does JWT Work?
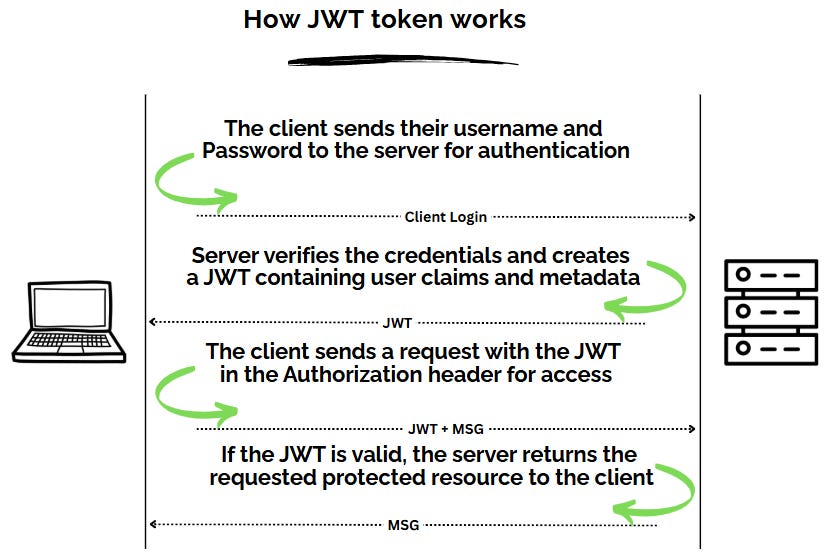
Let’s walk through a typical flow:
🔁 Step-by-step:
User logs in with valid credentials (username/password).
The server verifies them and creates a JWT containing user data (like
userId,role).This token is returned to the client (usually stored in localStorage or cookies).
For every subsequent request, the client sends this JWT in the
Authorizationheader:The server verifies the token’s signature and processes the request — no database lookup needed for every request!
✅ It’s fast.
✅ It’s secure (when done right).
✅ It scales beautifully with microservices.
🛠️ Implementing Unit of Work with EF Core
Let’s walk through a minimal but solid implementation
Create a Token Service
public class TokenService
{
private readonly string _secret;
private readonly string _issuer;
private readonly string _audience;
public TokenService(IConfiguration configuration)
{
_secret = configuration["Jwt:Key"];
_issuer = configuration["Jwt:Issuer"];
_audience = configuration["Jwt:Audience"];
}
public string GenerateJSONWebToken(string username)
{
var securityKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_secret));
var credentials = new SigningCredentials(securityKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var claims = new[] {
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, username),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Sub, ""),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Email, ""),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Jti, Guid.NewGuid().ToString())
};
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(_issuer,
_audience,
claims,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddHours(24),
signingCredentials: credentials);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
}
}Generate token by calling method
_tokenService.GenerateJSONWebToken("username")appsettings.json
"Jwt": {
"Key": "this is my custom Secret key for authentication",
"Issuer": "Test.com",
"Audience": "Test.com"
}🎯 Why Use JWT?
🔹 Stateless by Design : No session data stored on the server. Just decode the token and you’re good to go.
🔹 Scalable for Microservices : Each service can validate the token without relying on a centralized session store.
🔹 Frontend-Friendly : Perfect for SPAs and frontend frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.
🔹 Cross-Platform : Works across devices, domains, and environments — as long as the secret key or public/private key is shared.
🚨 JWT Use Cases
Here’s where JWT shines:
✅ API Authentication – Verify users in stateless REST APIs.
🔐 Role-based Authorization – Embed roles/permissions inside the payload.
🔁 Single Sign-On (SSO) – Share tokens between different services or applications.
🌍 Mobile App Auth – Secure user sessions on mobile without server state.
📦 Microservices Communication – Pass user claims between internal services.
🔐 Are JWTs Secure?
JWTs are secure if:
You use HTTPS (always).
You use strong signing algorithms like
HS256orRS256.You expire tokens (short-lived tokens + refresh strategy).
You never store sensitive data (like passwords) in the payload — it's base64 encoded, not encrypted.
🚀 Final Thoughts
JWTs have become a cornerstone of modern app security.
Whether you're building an API, a mobile app, or a full-stack web application, understanding JWTs will level up your authentication architecture.
So the next time someone asks how you secure your APIs, just smile and say:
“Stateless, token-based authentication with JWT.” 😎
I hope you found this guide helpful and informative.
Thanks for reading!
If you enjoyed this article, feel free to share it and follow me for more practical, developer-friendly content like this.
📁 GitHub Example
👉 Full working code available at:
🔗 http://sourcecode.kanaiyakatarmal.com/JWTAuth